Wineries
The classic method or méthode champenoise
 The classic method, also called méthode champenoise, takes its name from the French region of Champagne. It is a process of production of sparkling wine, which consists in inducing the refermentation in bottle of wines through the introduction of selected sugars and yeasts.
The classic method, also called méthode champenoise, takes its name from the French region of Champagne. It is a process of production of sparkling wine, which consists in inducing the refermentation in bottle of wines through the introduction of selected sugars and yeasts.
The spumantizzazione
The winemaking system to obtain a defined sparkling wine. Spumante is a special wine characterized by the high presence of carbon dioxide inside the bottle. There are two methods of sparkling wine: a classic method that can be used exclusively to indicate the production method of Champagne from 1 September 1994. And the: is divided into short charmat and long charmat.
Birth of the new wine
Also called still wine, it is obtained by pressing the grapes and separating the solid parts from the must. Generally the processing of the grapes takes place by separating them by type and by grape of origin.
At this point it is passed to a decanting operation in which the must is left in decantation for 12-24 hours. At this point the first fermentation is allowed to start, which lasts about 3 weeks and at the end the must is cooled to favor the fall of the deposits.
Assembling
The still wines are mixed together to get what the French call cuvée, ie a basic wine ready to become sparkling wine.
Bottling
The base wine is bottled with an addition of sugar syrup and selected yeasts. The bottles are capped with the crown cap. The counter-cap has a cylindrical shape with an open end and serves to contain the residues inside the bottle.
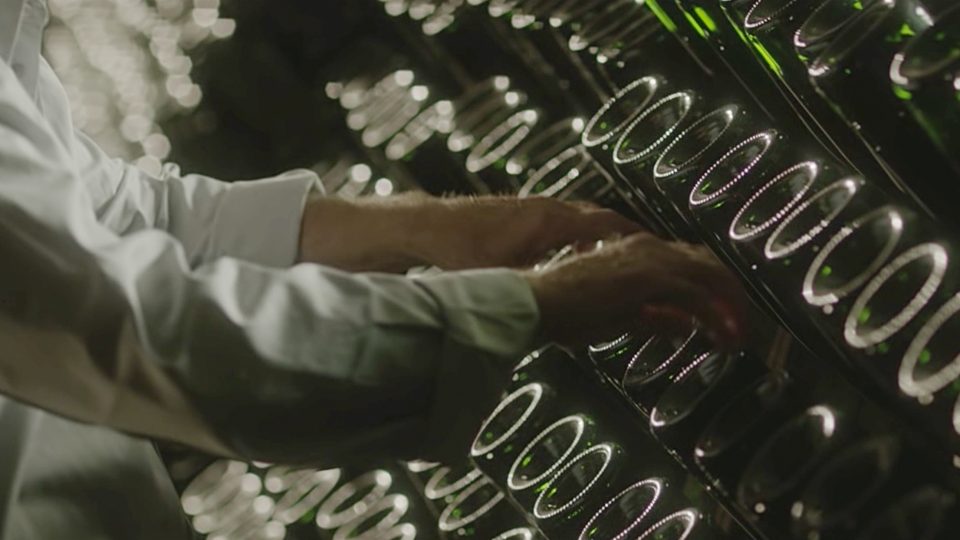
Takeover
The bottles are stacked, horizontally, inside cool and dark cellars. Here the refermentation in the bottle takes place, ie the yeasts transform the sugars into alcohol and carbon dioxide, which can not be dissolved in the air and will be absorbed by the wine and will be responsible for the sparkling perlage.
Refinement
Aging or aging has a duration ranging from a minimum of one year up to 5 years and even more for those vintage sparkling wines with high structural characteristics.
Shaking
It consists in threading the neck of the bottles in the holes present on easels called pupitre. The bottles will be turned with the end of the neck tending towards the bottom. Periodically the bottles will be shaken, turn a fraction of a turn and the inclination is increased. This phase aims to concentrate all the deposits and sediments created during the refinement on the cap.
Disgorging
Performed manually, straightening the bottle with one hand and with the other the crown cap is removed at the instant when the gas bubble, present in the bottle, laps the sediment plug. The disgorgement serves to remove the concentrated deposits on the cap.
Dosage
At this point the bottles are integrated with the part that has been lost with disgorgement. To fill the bottles are used sparkling wines of previous vintages and sugar syrup. Depending on the dosage of the liqueur d’expédition, you will have the different types of sparkling wines.
Capping and stabilization
After filling, the bottle is capped with a cork stopper (mushroom-shaped) and the protective cage is inserted around the cap. At this point the bottles undergo a light shaking to distribute the added liqueur evenly. Then you go to the washing of bottles and labeling. Finally, the bottles are returned to the cellar, so that the processing traumas are overcome and the wine is re-stabilized.
In the hope of having pleasantly caught your attention, I wish you a good day!
Ilde